Pointwise pairwise listwise
2025年9月22日
17:23
这3个都是用来learn to rank的,用来训练模型的排序能力的,3种宏观的训练范式,和用的模型是无关的,用biencoder或者crossencoder理论上都可以。
- Pointwise
In the pointwise approach, we treat the ranking problem as a simple classification task. For each query-document pair, we assign a target label that indicates the relevance of the document to the query. For example:
- Label 1 if the document is relevant.
- Label 0 if the document is not relevant.
Using our earlier example, the data would look like this:
q1,d1→label: 1
q1,d2→label: 0
q1,d3→label: 1
q2,d4→label: 0
q2,d5→label: 1
Pointwise的训练目标是让query和postive doc的得分是1,query和negative doc的得分是0
Pointwise的loss是query q和文档d的函数,即Loss = L(q,d,y),y表示label,值为0或1,常见的loss形式有:
二/多分类交叉熵损失,MSE,平滑 L1 损失(Smooth L1 Loss),另外,我觉得经典对比损失也是pointwise的,因为这里loss只用到了sample1和sample2,sample1相当于是query,sample2相当于是doc。

- Pairwise
The main drawback of the pointwise approach is that it misses the context in which the user interacts with a document. When a user clicks on or finds a document relevant, there are often multiple factors at play – one of the most important being the neighboring items.
For instance, if a user clicks on a document, it might not necessarily mean that the document is highly relevant. It could simply be that the other documents presented were of poor quality. Similarly, if you had shown a different set of documents for the same query, the user’s interaction might have been entirely different.
Pairwise的训练目标是让query和postive doc的得分/相似性/距离 大于/小于 query和negative doc的得分/相似性/距离 。
Pairwise的loss是query q和文档对d1,d2的函数,即Loss = L(q,d1,d2,y),y表示label,用于指示d1,d2是positve还是negative,常见的loss形式有:
- 交叉熵损失,ranknet用的就是交叉熵损失
- 三元损失(单个正例和单个负例),
loss_triplet = max(0, ||A - P||^2 - ||A - N||^2 + m)
- 合页损失
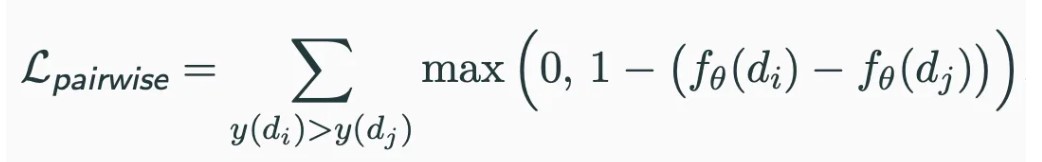
- InfoNCE loss/Multinegativerankingloss:单个正例和多个负例,但还是属于pairwise的方式,因为没有对整个排序列表做优化(不优化负样本之间的排序关系)

Pairwise的问题:One of the main challenges of implementing pairwise models is the computational complexity – since we need to compare all possible pairs of documents, the process scales as O(n²). Additionally, pairwise methods don’t consider the global ranking of documents;
3.Listwise
In listwise ranking, the goal is to optimize the entire list of documents based on their relevance to a query. Instead of treating individual documents separately, the focus is on the order in which they appear in the list.
listwise 的训练目标是让query和候选列表中的doc的相关性排序符合真实排序。
listwise 的loss是query q和文档列表d1,d2,d3…的函数,即Loss = L(q,d1,d2,d3,…Y),Y表示label,也是个列表,常见的loss形式有:
1. LambdaRank 损失
核心思想:
LambdaRank 的飞跃: LambdaRank 的作者发现,在计算完这个 Pairwise 的梯度 λ_ij 后,可以直接将其乘以一个与最终评价指标(如 NDCG(think of it as a way to measure how well the ordering of items matches their relevance. It rewards relevant items appearing at the top of the list and normalizes the score for easier comparison.))变化量相关的权重。
核心创新: 如果交换两个文档的位置能导致列表的 NDCG 大幅提升(例如,将一个高相关度的文档从底部提到顶部),那么这次交换的“重要性”就很大。因此,LambdaRank 会将对应的梯度 λ_ij 乘以一个很大的权重。反之,如果交换对 NDCG 影响很小,权重就小。直接优化排序评价指标,通过计算 “交换两个文档位置对指标的影响”(即 Lambda 值),将指标的 “改进空间” 转化为损失,指导模型调整分数。
2.交叉熵损失,也就是
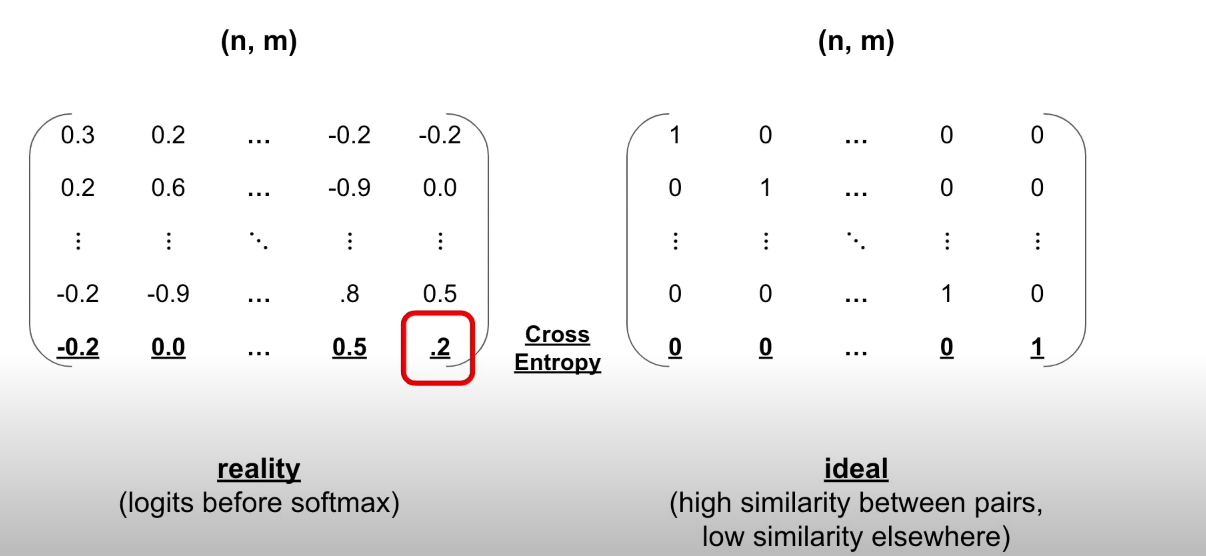
和对比学习的联系
|
特征 |
传统 LTR Pairwise (如 RankNet) |
对比学习 |
|
目标 |
学习一个排序函数(Scoring Function),用于对列表中的项目进行排序。 |
学习一个表征模型(Encoder),用于将数据映射到具有区分性的嵌入空间。 |
|
输出 |
一个可解释的分数(Score)。 |
一个高维的向量(Embedding)。 |
|
应用阶段 |
直接用于推理/预测。给定一个新文档,模型打出分,然后排序。 |
通常是一个预训练或表征学习阶段。学好的 Encoder 可以接一个简单的分类头或用于相似度检索。 |
|
监督信号 |
依赖于明确的、人工标注的相对顺序标签(如 DocA 比 DocB 更相关)。 |
通常依赖于数据本身构造的自监督信号(如一张图的两种增强视图互为正样本, batch 内其他图片为负样本)。 |
|
比较的维度 |
在分数空间进行比较。 |
在嵌入空间进行比较(通常使用余弦相似度或点积)。 |