Let's build GPT: from scratch, in code, spelled out.
2025年5月28日
13:50
- 关于Transformer的输入输出:
torch.manual_seed(1337)
batch_size = 4 # how many independent sequences will we process in parallel?
block_size = 8 # what is the maximum context length for predictions?
def get_batch(split):
# generate a small batch of data of inputs x and targets y
data = train_data if split == 'train' else val_data
ix = torch.randint(len(data) - block_size, (batch_size,))
x = torch.stack([data[i:i+block_size] for i in ix])
y = torch.stack([data[i+1:i+block_size+1] for i in ix])
return x, y
xb, yb = get_batch('train')
print('inputs:')
print(xb.shape)
print(xb)
print('targets:')
print(yb.shape)
print(yb)
print('----')
for b in range(batch_size): # batch dimension
for t in range(block_size): # time dimension
context = xb[b, :t+1]
target = yb[b,t]
print(f"when input is {context.tolist()} the target: {target}")
inputs:
torch.Size([4, 8])
tensor([[24, 43, 58, 5, 57, 1, 46, 43],
[44, 53, 56, 1, 58, 46, 39, 58],
[52, 58, 1, 58, 46, 39, 58, 1],
[25, 17, 27, 10, 0, 21,
1, 54]])
targets:
torch.Size([4, 8])
tensor([[43, 58, 5, 57, 1, 46, 43, 39],
[53, 56, 1, 58, 46, 39, 58, 1],
[58, 1, 58, 46, 39, 58, 1, 46],
[17, 27, 10, 0, 21,
1, 54, 39]])
----
when input is [24] the target: 43
when input is [24, 43] the target: 58
when input is [24, 43, 58] the target: 5
when input is [24, 43, 58, 5] the target: 57
when input is [24, 43, 58, 5, 57] the target: 1
when input is [24, 43, 58, 5, 57, 1] the target: 46
when input is [24, 43, 58, 5, 57, 1, 46] the target: 43
when input is [24, 43, 58, 5, 57, 1, 46, 43] the target: 39
when input is [44] the target: 53
when input is [44, 53] the target: 56
when input is [44, 53, 56] the target: 1
when input is [44, 53, 56, 1] the target: 58
when input is [44, 53, 56, 1, 58] the target: 46
when input is [44, 53, 56, 1, 58, 46] the target: 39
when input is [44, 53, 56, 1, 58, 46, 39] the target: 58
when input is [44, 53, 56, 1, 58, 46, 39, 58] the target:
将X和y中的token整数索引替换为token的embedding,X和y的Shape就是3维的,shape = B,T,C, B=batch_size, T是上下文长度,C是channel,即embedding的长度。
- 优化平均值的计算
X的shape为 B,T,C,对于batch中的单个样本来说,当想要计算当前位置t的前面所有的token的embedding的平均值时,即
# We want x[b,t] = mean_{i<=t} x[b,i]
1)直接的方法是:
xbow = torch.zeros((B,T,C))
for b in range(B):
for t in range(T):
xprev = x[b,:t+1] # (t,C)
xbow[b,t] = torch.mean(xprev, 0)
2)还可以通过矩阵相乘来实现优化:
# version 2: using matrix multiply for a weighted aggregation
wei = torch.tril(torch.ones(T, T)) # 下三角矩阵
wei = wei / wei.sum(1, keepdim=True)
xbow2 = wei @ x # (B, T, T) @ (B, T, C) ----> (B, T, C) 这里是batch matrix multiplication,
torch.allclose(xbow, xbow2)
wei 是个 下三角矩阵:array([[1. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. ],
[0.5 , 0.5 , 0. , 0. , 0. ],
[0.33333333, 0.33333333, 0.33333333, 0. , 0. ],
[0.25 , 0.25 , 0.25 , 0.25 , 0. ],
[0.2 , 0.2 , 0.2 , 0.2 , 0.2 ]])
3)第三种方式是用mask_fill+softmax
# version 3: use Softmax
tril = torch.tril(torch.ones(T, T))
wei = torch.zeros((T,T)) # 这行表示how much of each token from past do we want to aggregate
wei = wei.masked_fill(tril == 0, float('-inf')) # 这行表示token只能和past tokens交互
wei = F.softmax(wei, dim=-1)
xbow3 = wei @ x
torch.allclose(xbow, xbow3)
- Attention Block
关于attention的理解,different tokens will find different other tokens more or less interesting, and we want that to be data dependent, 也就是根据数据,来决定对其他token的关注度。如何自适应数据,决定对其他token的关注度呢?
Every token at each position will emit two vectors, a query and a key, the query roughly speaking what I am looking for, and the key is what do I contain. The affinities between tokens(也就是token之间的交互强度) is the dot product
of key and query. So if the key and query are aligned, they will interact to a very high amount .
# version 4: self-attention!
torch.manual_seed(1337)
B,T,C = 4,8,32 # batch, time, channels
x = torch.randn(B,T,C)
# let's see a single Head perform self-attention
head_size = 16
key = nn.Linear(C, head_size, bias=False)
query = nn.Linear(C, head_size, bias=False)
value = nn.Linear(C, head_size, bias=False)
k = key(x) # (B, T, 16)
q = query(x) # (B, T, 16)
wei = q @ k.transpose(-2, -1) # (B, T, 16) @ (B, 16, T) ---> (B, T, T)
tril = torch.tril(torch.ones(T, T))
#wei = torch.zeros((T,T))
wei = wei.masked_fill(tril == 0, float('-inf'))
wei = F.softmax(wei, dim=-1)
v = value(x)
out = wei @ v
#out = wei @ x
out.shape
Attention is a communication mechanism. Can be seen as nodes in a directed graph looking at each other and aggregating information with a weighted sum from all nodes that point to them, with data-dependent weights. 类比:有向图中节点的汇聚。
"Scaled" attention additional divides wei by 1/sqrt(head_size). This makes it so when input Q,K are unit variance, wei will be unit variance too and Softmax will stay diffuse and not saturate too much. Illustration below。
Attention = 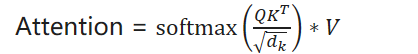
为什么要除以根号dk呢,
k = torch.randn(B,T,head_size)
q = torch.randn(B,T,head_size)
wei = q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)
k,q都是方差为1的正态分布,但是k*q的方差不是1,类似于神经网络初始化权重时,进行normalization一样:self.weight = torch.randn((fan_in, fan_out), generator=g) / fan_in**0.5.
那么为什么要方差为1的分布呢,因为如果wei的方差过大,即wei的分布不是均匀的,那么经过softmax后,会出现占主导地位的值,例如,
print(torch.softmax(torch.tensor([0.1, -0.2, 0.3, -0.2, 0.5]), dim=-1) )
tensor([0.1925, 0.1426, 0.2351, 0.1426, 0.2872]) # 分布比较均匀
而如果某个值过大,经过softmax后,概率也会变得很大,如0.8,
print(torch.softmax(torch.tensor([0.1, -0.2, 0.3, -0.2, 0.5])*8, dim=-1) )# gets too peaky, converges to one-hot
tensor([0.0326, 0.0030, 0.1615, 0.0030, 0.8000]) # 分布不均匀
这样的情况不利用aggregate,尤其是在初始化的阶段。
- 整体代码
Transformer中采取的两个措施来解决深度神经网络训练困难的问题:1.残差连接 2.layernorm

batch_size = 16 # how many independent sequences will we process in parallel?
block_size = 32 # what is the maximum context length for predictions?
max_iters = 5000
eval_interval = 100
learning_rate = 1e-3
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
eval_iters = 200
n_embd = 64
n_head = 4
n_layer = 4
dropout = 0.0
class Head(nn.Module):
""" one head of self-attention """
def __init__(self, head_size):
super().__init__()
self.key = nn.Linear(n_embd, head_size, bias=False)
self.query = nn.Linear(n_embd, head_size, bias=False)
self.value = nn.Linear(n_embd, head_size, bias=False)
self.register_buffer('tril', torch.tril(torch.ones(block_size, block_size)))
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, x):
B,T,C = x.shape
k = self.key(x) # (B,T,C)
q = self.query(x) # (B,T,C)
# compute attention scores ("affinities")
wei = q @ k.transpose(-2,-1) * C**-0.5 # (B, T, C) @ (B, C, T) -> (B, T, T)
wei = wei.masked_fill(self.tril[:T, :T] == 0, float('-inf')) # (B, T, T)
wei = F.softmax(wei, dim=-1) # (B, T, T)
wei = self.dropout(wei)
# perform the weighted aggregation of the values
v = self.value(x) # (B,T,C)
out = wei @ v # (B, T, T) @ (B, T, C) -> (B, T, C)
return out
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
""" multiple heads of self-attention in parallel """
def __init__(self, num_heads, head_size):
super().__init__()
self.heads = nn.ModuleList([Head(head_size) for _ in range(num_heads)])
self.proj = nn.Linear(n_embd, n_embd) # 这里还有个projection层,对多个头的concated attention value进行线性变换,也就是将n个头concat的结果投影回原来的token的embedding维度。
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, x):
out = torch.cat([h(x) for h in self.heads], dim=-1) # 多头注意力是将多个头concat起来,所以attention value的维度是原来的n_head分之一,这样concat之后的长度才和原来的embedding一致。
out = self.dropout(self.proj(out))
return out
class FeedFoward(nn.Module): # 前馈层对每个token单独独立处理的,不存在attention中的交互。
""" a simple linear layer followed by a non-linearity """
def __init__(self, n_embd):
super().__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(n_embd, 4 * n_embd), # 这里前馈层先将每个token的embedding的长度扩大4倍
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(4 * n_embd, n_embd), # 这里还有个projection层,投影回原来token的embedding的长度。
nn.Dropout(dropout),
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.net(x)
class Block(nn.Module): #Block是多头注意力+前馈层的组合
""" Transformer block: communication followed by computation """
def __init__(self, n_embd, n_head):
# n_embd: embedding dimension, n_head: the number of heads we'd like
super().__init__()
head_size = n_embd // n_head
self.sa = MultiHeadAttention(n_head, head_size)
self.ffwd = FeedFoward(n_embd)
self.ln1 = nn.LayerNorm(n_embd)
self.ln2 = nn.LayerNorm(n_embd)
def forward(self, x):
x = x + self.sa(self.ln1(x)) #block中加入残差连接,因为深度神经网络的训练困难,为什么可以缓解:因为提供了另一个path,使得输入对输出的影响不只有一条path,也就是输入的梯度不会变为0,类似的还有LSTM中的各种门,也是提供了不同的path,使得某个path无法占主导地位或完全没有作用。
x = x + self.ffwd(self.ln2(x)) # 两个残差连接, 一个是多头注意力,一个是前馈
#两个layernorm分别在多头注意力层和前馈层之前,而不是之后 。这和上面那张原始的Transformer论文中的图不一样
return x
# super simple bigram model
class BigramLanguageModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# each token directly reads off the logits for the next token from a lookup table
self.token_embedding_table = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, n_embd)
self.position_embedding_table = nn.Embedding(block_size, n_embd)
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*[Block(n_embd, n_head=n_head) for _ in range(n_layer)])
self.ln_f = nn.LayerNorm(n_embd) # final layer norm
self.lm_head = nn.Linear(n_embd, vocab_size)
def forward(self, idx, targets=None):
B, T = idx.shape
# idx and targets are both (B,T) tensor of integers
tok_emb = self.token_embedding_table(idx) # (B,T,C)
pos_emb = self.position_embedding_table(torch.arange(T, device=device)) # (T,C)
x = tok_emb + pos_emb # (B,T,C)
x = self.blocks(x) # (B,T,C)
x = self.ln_f(x) # (B,T,C) blocks层之后也加入layernorm层
logits = self.lm_head(x) # (B,T,vocab_size)
if targets is None:
loss = None
else:
B, T, C = logits.shape
logits = logits.view(B*T, C)
targets = targets.view(B*T)
loss = F.cross_entropy(logits, targets)
return logits, loss
def generate(self, idx, max_new_tokens):
# idx is (B, T) array of indices in the current context
for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
# crop idx to the last block_size tokens
idx_cond = idx[:, -block_size:]
# get the predictions
logits, loss = self(idx_cond)
# focus only on the last time step
logits = logits[:, -1, :] # becomes (B, C)
# apply softmax to get probabilities
probs = F.softmax(logits, dim=-1) # (B, C)
# sample from the distribution
idx_next = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=1) # (B, 1)
# append sampled index to the running sequence
idx = torch.cat((idx, idx_next), dim=1) # (B, T+1)
return idx