RAG
2025年8月1日
19:15
1.Query translation
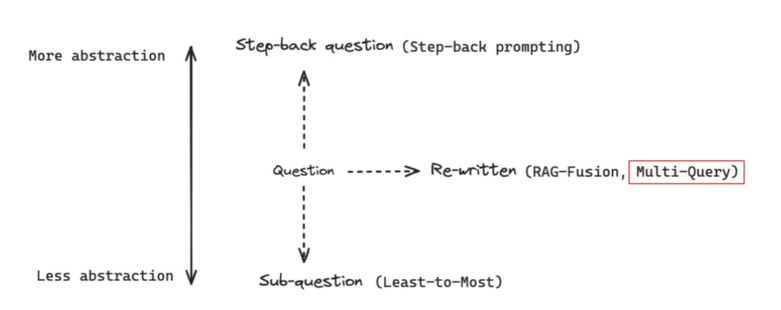
Query translation是advanced RAG的第一个stage,将用户的原始query转换成更利于retrieval的query。用户的query有可能是ambigous模糊的,低质量的query是不利于语义搜索的,无法retrieve到正确的documents。
有几种方式来优化用户query,如下图所示。
可以将question分解成子问题,独立解决子问题,更具体的层面 ;可以将问题变为higher level question,更抽象的层面;可以将问题进行rewrite。
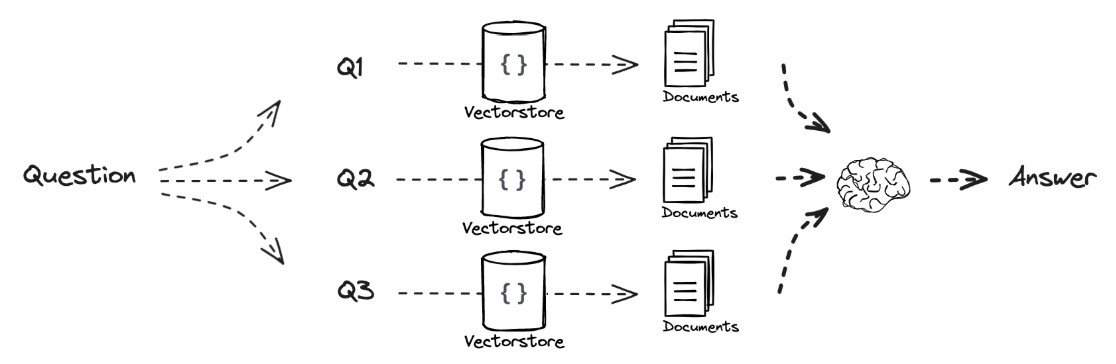
1)Multi query
Transform a question into multiple perspectives。将问题进行多个角度的重写,然后retrieve on each question。目的是提高retrieve到正确documents的概率。
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
# Multi Query: Different Perspectives
#利用LLM生成多个perspective的query
template =
"""You are an AI language
model assistant. Your task is to generate five
different versions of the given user
question to retrieve relevant documents from a vector
database. By generating multiple
perspectives on the user question, your goal is to help
the user overcome some of the limitations of
the distance-based similarity search.
Provide these alternative questions
separated by newlines. Original question: {question}"""
prompt_perspectives = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
from
langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
generate_queries = (
prompt_perspectives
| ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
| StrOutputParser()
| (lambda
x: x.split("\n"))
)
from langchain.load import dumps, loads
#多个query检索出来的documents进行unique_union合并。
def
get_unique_union(documents: list[list]):
"""
Unique union of retrieved docs """
# Flatten list of lists, and convert each Document to string
flattened_docs = [dumps(doc) for
sublist in documents for doc in
sublist]
# Get unique documents
unique_docs =
list(set(flattened_docs))
# Return
return [loads(doc) for
doc in unique_docs]
# Retrieve
question = "What is task decomposition for LLM agents?"
retrieval_chain = generate_queries | retriever.map() | get_unique_union
docs = retrieval_chain.invoke({"question":question})
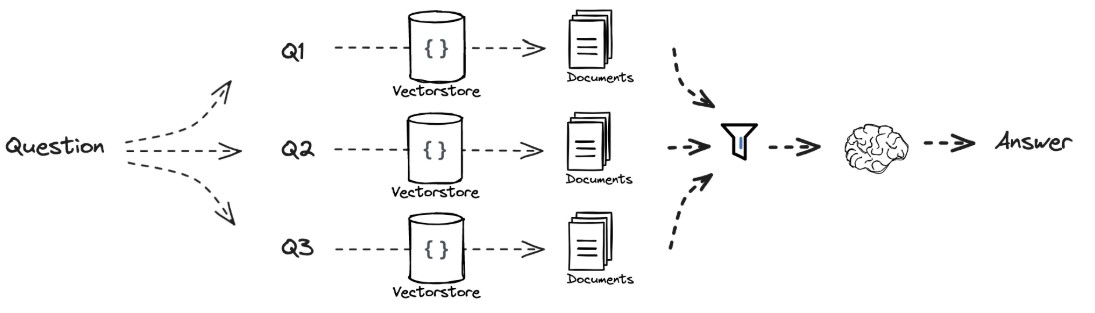
2)RAG Fusion
multi query的唯一区别就是多了对检索到的文档进行重要性排序。
from langchain.load import dumps, loads
def
reciprocal_rank_fusion(results: list[list], k=60):
"""
Reciprocal_rank_fusion that takes multiple lists of ranked documents
and an optional parameter k used in the RRF formula """
# Initialize a dictionary to hold fused scores for each unique
document
fused_scores = {}
# Iterate through each list of ranked
documents
for docs in
results:
# Iterate through each document in the list, with its
rank (position in the list)
for rank, doc in
enumerate(docs):
# Convert the document to a string
format to use as a key (assumes documents can be serialized to JSON)
doc_str =
dumps(doc)
# If the document is not yet in the
fused_scores dictionary, add it with an initial score of 0
if
doc_str not in fused_scores:
fused_scores[doc_str] = 0
# Retrieve the current score of the
document, if any
previous_score =
fused_scores[doc_str]
# Update the score of the document
using the RRF formula: 1 / (rank + k)
fused_scores[doc_str] += 1 / (rank + k)
# Sort the documents based on their
fused scores in descending order to get the final reranked results
reranked_results = [
(loads(doc), score)
for doc, score in
sorted(fused_scores.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
]
# Return the reranked results as a list
of tuples, each containing the document and its fused score
return reranked_results
retrieval_chain_rag_fusion = generate_queries |
retriever.map() |
reciprocal_rank_fusion
docs = retrieval_chain_rag_fusion.invoke({"question": question})
len(docs)
3)Decomposition
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
# Decomposition
template = """You are a helpful assistant that
generates multiple sub-questions related to an input question. \n
The goal is to break down the input into a
set of sub-problems / sub-questions that can be answers in isolation. \n
Generate multiple search queries related to:
{question} \n
Output (3 queries):"""
prompt_decomposition = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
分解成子问题后,后续有2种方式:
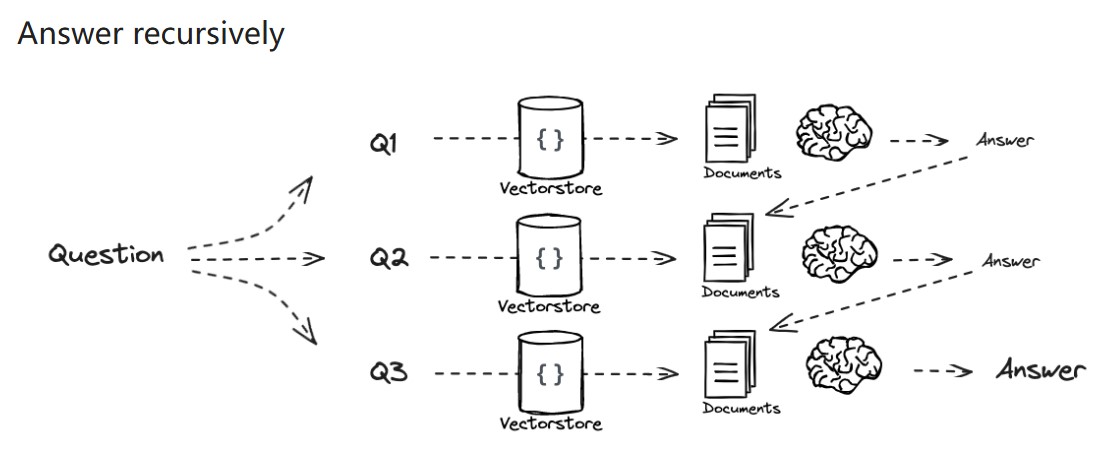
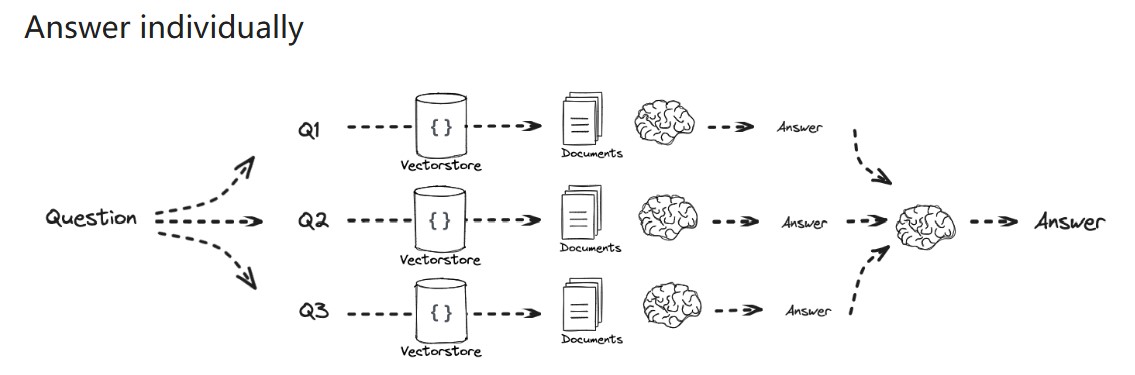
4)Step back
# Few Shot Examples
from langchain_core.prompts import
ChatPromptTemplate, FewShotChatMessagePromptTemplate
examples = [
{
"input": "Could the
members of The Police perform lawful arrests?",
"output": "what can the
members of The Police do?",
},
{
"input": "Jan Sindel’s
was born in what country?",
"output": "what is Jan
Sindel’s personal history?",
},
]
# We now transform these
to example messages
example_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("human", "{input}"),
("ai", "{output}"),
]
)
few_shot_prompt = FewShotChatMessagePromptTemplate(
example_prompt=example_prompt,
examples=examples,
)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
(
"system",
"""You are an expert at world knowledge.
Your task is to step back and paraphrase a question to a more generic step-back
question, which is easier to answer. Here are a few examples:""",
),
# Few shot examples
few_shot_prompt,
# New question
("user", "{question}"),
]
)
generate_queries_step_back = prompt |
ChatOpenAI(temperature=0) | StrOutputParser()
question = "What is task decomposition for LLM agents?"
generate_queries_step_back.invoke({"question": question})
# Response prompt
response_prompt_template = """You are an expert of world knowledge. I
am going to ask you a question. Your response should be comprehensive and not
contradicted with the following context if they are relevant. Otherwise, ignore
them if they are not relevant.
# {normal_context}
# {step_back_context}
# Original Question: {question}
# Answer:"""
response_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(response_prompt_template)
#不但提供normal_context(原始query的retrieval结果),还提供step_back_context(step_back问题的retrieval结果)
chain =
(
{
# Retrieve context using the normal question
"normal_context": RunnableLambda(lambda x: x["question"]) | retriever,
# Retrieve context using the step-back question
"step_back_context":
generate_queries_step_back | retriever,
# Pass on the question
"question": lambda x: x["question"],
}
| response_prompt
| ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
| StrOutputParser()
)
chain.invoke({"question": question})
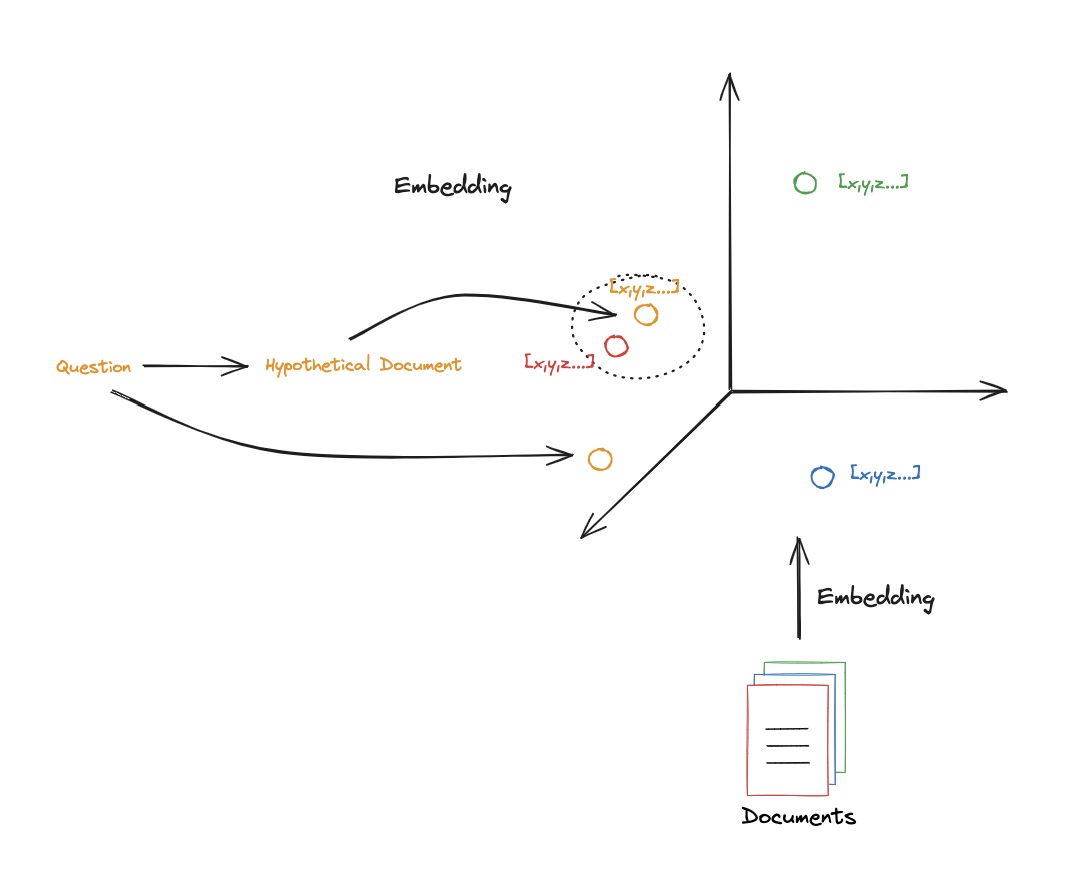
5)HyDE
retrieval时需要计算query embedding和documents embedding的相似度,但query和documents可能是很不同的,query可能很短,documents可能比较长。
将query转化成一个假设的document,这个假设的document在doc 空间中和 target document更近,更利于retrieval。
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
# HyDE document generation
#直接让LLM根据用户question生成一篇passage,然后用这篇passage进行检索
template =
"""Please write a scientific
paper passage to answer the question
Question: {question}
Passage:"""
prompt_hyde = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
from
langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
generate_docs_for_retrieval = (
prompt_hyde |
ChatOpenAI(temperature=0) | StrOutputParser()
)
# Run
question = "What is task decomposition for LLM agents?"
generate_docs_for_retrieval.invoke({"question":question})
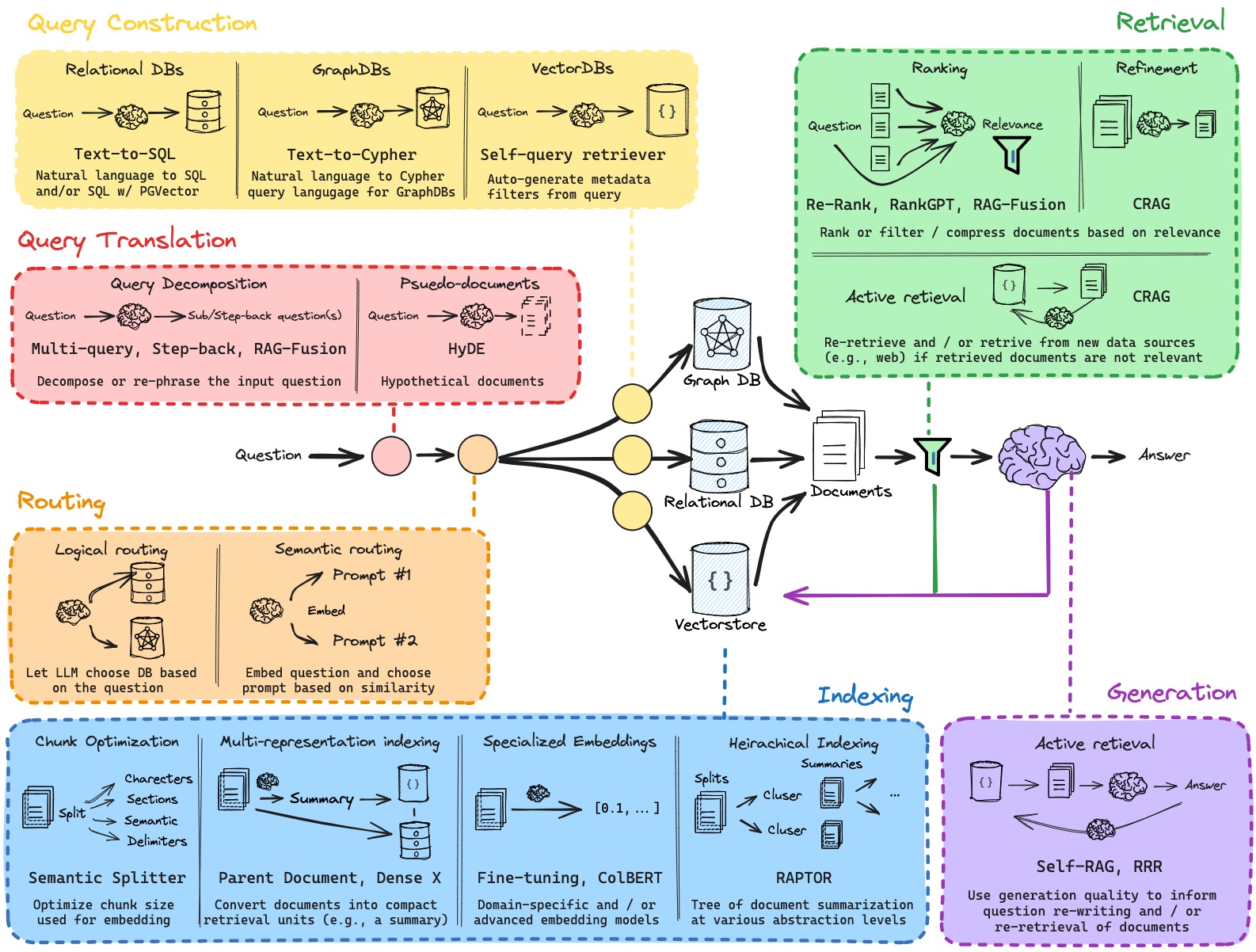
2.Routing
有多个数据库,如图数据库,关系数据库,Vector store等,让LLM根据用户question选择对哪个数据库进行retrieve。
3.Query Construction
将用户query转成数据库的语言,如对于关系数据库需要text to sql,对于Vectore store可以进行metadata filter。
self query retriever:也就是,有时候并不需要进行语义搜索,而是只需要对vector store中的metadata进行一次lookup即可。本质上就是进行一次数据库查询操作。
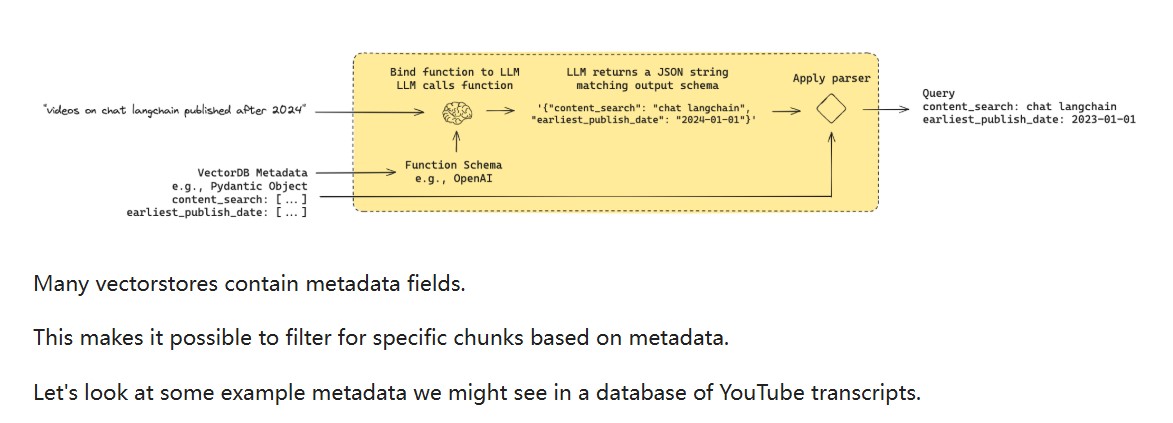
4.Indexing
关于Indexing,Indexing是根据query,从数据库中检索出相关documents的这部分操作,可以看成是初步的retrieval。而retrieval是根据indexing的结果,进一步加工的操作,如对初步检索出来的documents进行ranking, refinement,再检索等等。
1)Multi-representation Indexing
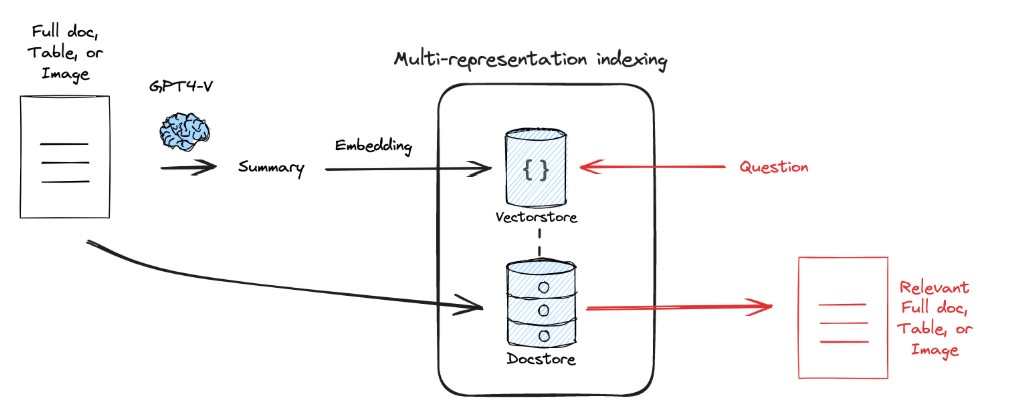
将原始文档进行summary或distillation,用summary的embedding和query embedding进行匹配。
2)RAPTOR
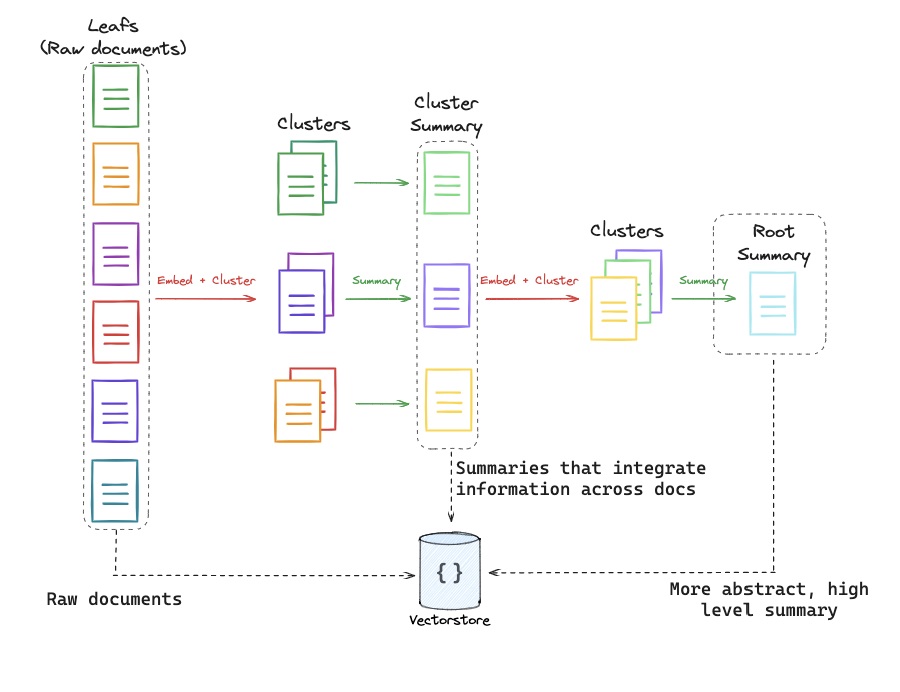
3) ColBERT,还有BGE用的sparse , multi , hybrid retrieval
RAGatouille makes it as simple to use ColBERT.
ColBERT generates a contextually influenced vector for each token in the passages.
ColBERT similarly generates vectors for each token in the query.
Then, the score of each document is the sum of the maximum similarity of each query embedding to any of the document embeddings.
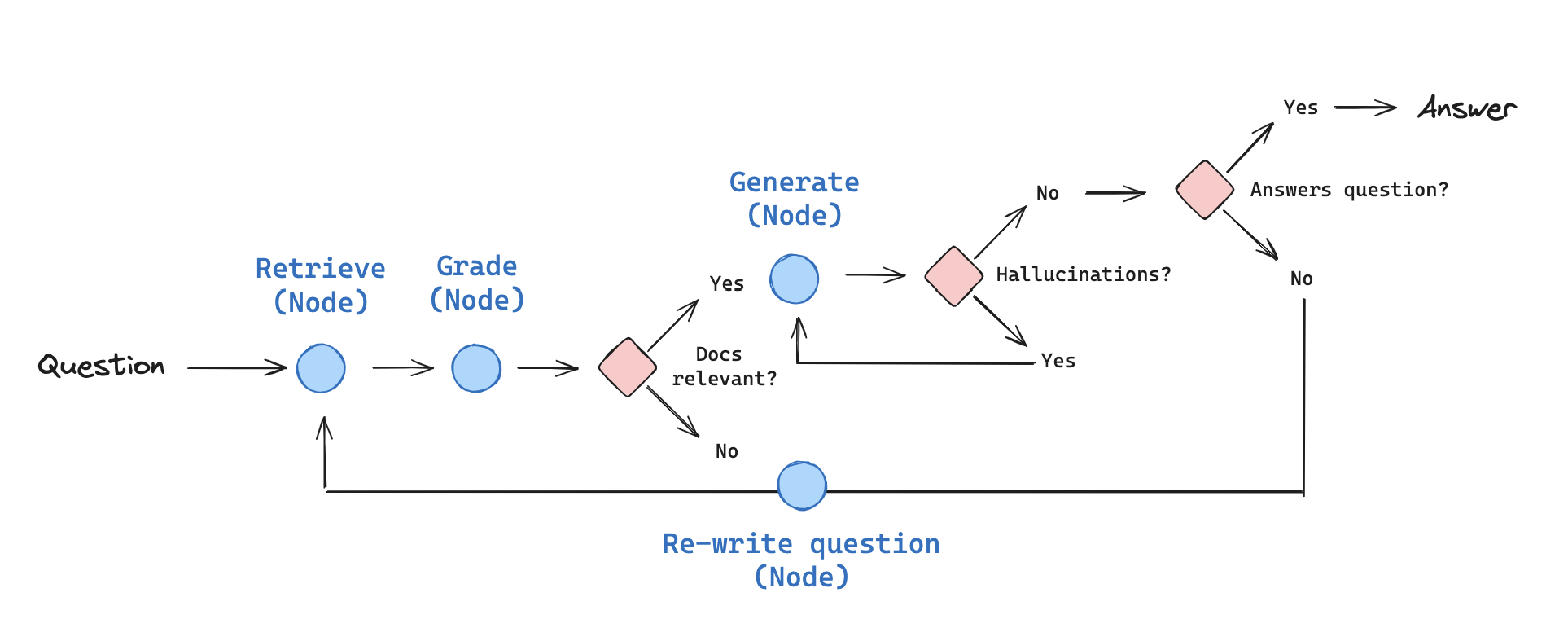
5.CRAG
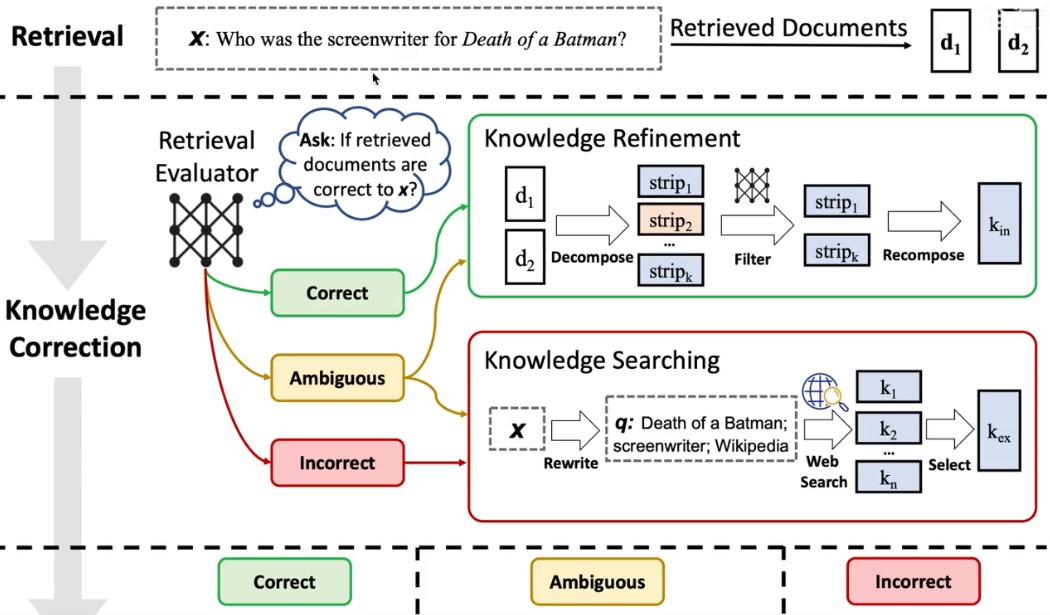
CRAG 主要透過「Retrieval Evaluator (檢索評估器)」與「Knowledge Refinement (知識精練)」兩個方法來實現更好的回應結果。
- Retrieval
Evaluator(檢索評估器)
用於評估針對特定問題檢索到的文件的整體品質。它還會利用網路搜索作為輔助工具,進一步提升檢索結果的品質。評估答案分為「正確」(correct)、「模糊」(Ambiguous)、「錯誤」(Incorrect)三種情況。對於「正確」的情況,直接進行知識精練,抽取關鍵資訊。針對「錯誤」的資訊,則利用網路檢索來擴充知識量。針對「模糊」的知識,結合前面兩種操作來提供答案的穩健性及精準度。 - Knowledge
Refinement(知識精練)
先將文件進行分解再重新組合,以便深入挖掘文件中的核心知識點。利用自訂規則將文件進行分解,並由檢索評估器來衡量其相關性。最後將剩餘的相關知識重新整合。
CRAG的发生在retrieval阶段的最后开始,即当我们获得到了近似的document(或者说relevant snippets)之后。
然后我们会进入一个额外的环节,叫Knowledge Correction。在这里呢我们会先对retrieval得到的每一个相关切片snippets进行evaluate,评估一下我们获取到的snippet是不是对问的问题有效?(此处重点:evaluator也是一个LLM)
然后会有三种情况:
Correct:那就直接进行RAG的正常流程。(不过图中是加了进一步的优化)
Incorrect:那就直接丢弃掉原来的document,直接去web里搜索相关信息
Ambiguous:对于模糊不清的,就两种方式都要
那么在最后的generation部分,也是根据三种不同的情况分别做处理。
Correct:那现在就直接拼接问题和相关文档
Incorrect:那现在就直接拼接问题和web获取的信息
Ambiguous:,那现在就拼接三个加起来
Langchain版流程图:
简单一句话,如果检索的doc不相关,就进行web search。
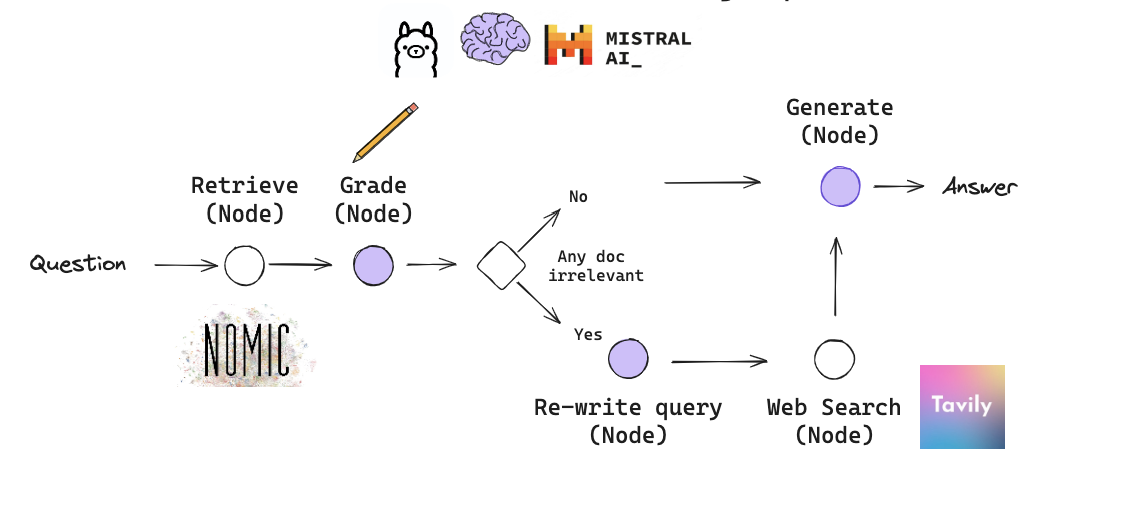
6.Self-RAG
和CRAG的核心都是self-reflective,即当我发现结果不是那么有效时,我要通过环回溯到之前的步骤去优化。
和CRAG不一样的是,selfRAG的流程是从Retrieve node就开始进行的,大概流程: