Lora
2025年6月10日
14:01
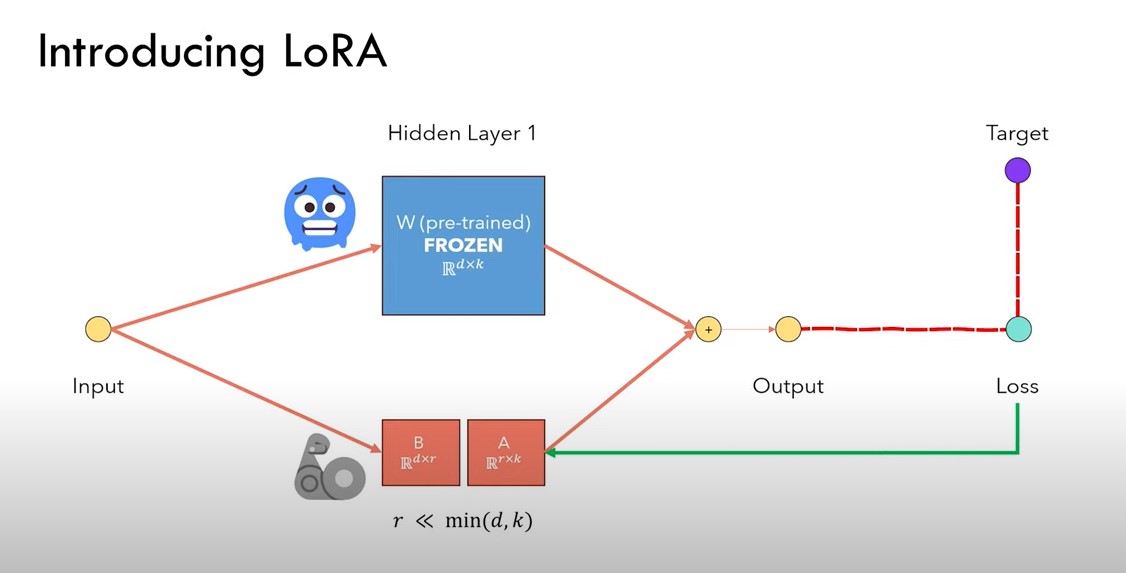
前向计算时,原来y=W*x ,加入lora后,y=W*x+BA*X = (W+BA)*x,
反向传播时,W的参数冻结,只调整B和A的参数。
Pytorch实现:
class
LoRAParametrization(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, features_in, features_out, rank=1, alpha=1, device='cpu'):
super().__init__()
# Section 4.1 of the paper:
# We use a random
Gaussian initialization for A and zero for B, so ∆W = BA is zero at the
beginning of training
self.lora_A
= nn.Parameter(torch.zeros((rank,features_out)).to(device))
self.lora_B
= nn.Parameter(torch.zeros((features_in, rank)).to(device))
nn.init.normal_(self.lora_A, mean=0, std=1)
# Section 4.1 of the paper:
# We then scale
∆Wx by α/r , where α is a constant in r.
# When optimizing
with Adam, tuning α is roughly the same as tuning the learning rate if we scale
the initialization appropriately.
# As a result, we
simply set α to the first r we try and do not tune it.
# This scaling
helps to reduce the need to retune hyperparameters when we vary r.
self.scale
= alpha / rank
self.enabled
= True
def
forward(self, original_weights):
if self.enabled:
# Return W + (B*A)*scale
return
original_weights + torch.matmul(self.lora_B, self.lora_A).view(original_weights.shape) * self.scale
else:
return
original_weights
Add the parameterization to our network.
import torch.nn.utils.parametrize as parametrize
def
linear_layer_parameterization(layer, device, rank=1, lora_alpha=1):
# Only add the parameterization to the weight matrix, ignore the
Bias
# From section 4.2 of the paper:
# We limit our study to
only adapting the attention weights for downstream tasks and freeze the MLP
modules (so they are not trained in downstream tasks) both for simplicity and
parameter-efficiency.
# [...]
# We leave the empirical
investigation of [...], and biases to a future work.
features_in, features_out =
layer.weight.shape
return LoRAParametrization(
features_in, features_out, rank=rank, alpha=lora_alpha, device=device
)
parametrize.register_parametrization(
net.linear1, "weight",
linear_layer_parameterization(net.linear1, device)
)
parametrize.register_parametrization(
net.linear2, "weight",
linear_layer_parameterization(net.linear2, device)
)
parametrize.register_parametrization(
net.linear3, "weight",
linear_layer_parameterization(net.linear3, device)
)
def
enable_disable_lora(enabled=True):
for layer in [net.linear1, net.linear2, net.linear3]:
layer.parametrizations["weight"][0].enabled = enabled
Freeze all the parameters of the original network and only fine tuning the ones introduced by LoRA. Then fine-tune the model on the digit 9 and only for 100 batches.
# Freeze the non-Lora parameters
for name, param in net.named_parameters():
if 'lora' not in
name:
print(f'Freezing non-LoRA
parameter {name}')
param.requires_grad
= False
# Load the MNIST dataset again, by
keeping only the digit 9
mnist_trainset = datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
exclude_indices = mnist_trainset.targets == 9
mnist_trainset.data = mnist_trainset.data[exclude_indices]
mnist_trainset.targets = mnist_trainset.targets[exclude_indices]
# Create a dataloader for
the training
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(mnist_trainset, batch_size=10, shuffle=True)
# Train the network with LoRA only on
the digit 9 and only for 100 batches (hoping that it would improve the
performance on the digit 9)
train(train_loader, net, epochs=1,
total_iterations_limit=100)
关于task_type参数:
https://discuss.huggingface.co/t/task-type-parameter-of-loraconfig/52879/6
task_type影响的是返回的peft model的类型。
The task_type parameter is used in the superclass PeftConfig。
Late reply but I was wondering the same and could not find details in the doc so I put an answer here.
Based on Peft git repo, it seems that the model class returned by get_peft_model(peft_config)
depends on this value :
peft/src/peft/mapping , with the following mapping Line 81 :
MODEL_TYPE_TO_PEFT_MODEL_MAPPING: dict[str, type[PeftModel]] = {
"SEQ_CLS": PeftModelForSequenceClassification,
"SEQ_2_SEQ_LM": PeftModelForSeq2SeqLM,
"CAUSAL_LM": PeftModelForCausalLM,
"TOKEN_CLS": PeftModelForTokenClassification,
"QUESTION_ANS": PeftModelForQuestionAnswering,
"FEATURE_EXTRACTION": PeftModelForFeatureExtraction,
}
If you do not specify a value, you get a default PeftModel (Lines 210-220)
if peft_config.task_type not in
MODEL_TYPE_TO_PEFT_MODEL_MAPPING.keys() and not
peft_config.is_prompt_learning:
return PeftModel(
model,
peft_config,
adapter_name=adapter_name,
autocast_adapter_dtype=autocast_adapter_dtype,
low_cpu_mem_usage=low_cpu_mem_usage,
)
if
peft_config.is_prompt_learning:
peft_config =
_prepare_prompt_learning_config(peft_config, model_config)
return
MODEL_TYPE_TO_PEFT_MODEL_MAPPING[peft_config.task_type](
model, peft_config,
adapter_name=adapter_name,
autocast_adapter_dtype=autocast_adapter_dtype
)
Finally it seems that in the case where task_type=SEQ_CLS , the classifier heads are excluded from LoRA : in peft/src/peft/tuners/tuner_utils:
if output_emb is not None:
# ignore the last classification head for text generation
models
last_module_name = [name for name, module in
model.named_modules() if module is output_emb][0]
module_names_to_exclude.add(last_module_name)
elif peft_config.task_type == TaskType.SEQ_CLS:
# ignore classifier head for classification models (issue
2027)
# there is no fix name for the classifier head, so check
the common ones
for name in SEQ_CLS_HEAD_NAMES:
cls_head = getattr(model, name, None)
if cls_head is not None:
last_module_name = [name for name, module in
model.named_modules() if module is cls_head][0]
module_names_to_exclude.add(last_module_name)
break
and also the number of transformer_submodules increases from 1 to 2 in the case of SEQ_2_SEQ_LM (in peft/src/peft/peft_model.py):
if config.num_transformer_submodules is None:
config.num_transformer_submodules
= 2 if config.task_type == TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM else 1