CS336-2025-lec10
2025年10月29日
15:17
- Time-to-first-token (TTFT): how long user waits before any generation happens (matters for interactive applications)
- Latency (seconds/token): how fast tokens appear for a user (matters for interactive applications)
- Throughput (tokens/second): useful for batch processing applications
- Training (supervised): you see all tokens, can parallelize over sequence (matmul in Transformer)
- Inference: you have to generate sequentially, can't parallelize, so harder to fully utilize compute
- Prefill: given a prompt, encode into vectors (parallelizable like in training)
- Generation: generate new response tokens (sequential)
- Prefill: easy to make compute-limited (good) by making B T large enough
- Generation:
- Generating one token at a time (T = 1)
- B is number of concurrent requests, hard to make large enough
- In MLP layers, every sequence hits the same MLP weights (Wup, Wgate, Wdown don't depend on B)
- In attention layers, every sequence has its own vectors KV cache (Q, K, V all depend on B)
- Prefill is compute-limited, generation is memory-limited
- MLP intensity is B (requires concurrent requests), attention intensity is 1 (impossible to improve)
- Smaller batch sizes yields better latency but worse throughput,小的batchsize,latency变小了,但是吞吐量变小
- Larger batch sizes yields better throughput but worse latency,大的batchsize,latency变大了,但是吞吐量变大
- Goal: reduce the KV cache size (since inference is memory-limited) without hurting accuracy
- Lower-dimensional KV cache (GQA, MLA, shared KV cache)
- Local attention on some of the layers
- Kernel to fuse block read and attention (reduce kernel launch overhead)
- Use latest kernels (FlashAttention, FlashDecoding)
- Use CUDA graphs to avoid kernel launch overhead
Inference
Inference: given a fixed model, generate responses given prompts
Metrics:
Key considerations in efficiency:
KV cache: for every sequence (B), token (S), layer (L), head (K), store an H-dimensional vector
Two stages of inference:
推理时的2个步骤,先是对prompt部分进行encode,再生成下一个token
Let's compute the FLOPs and memory IO for both the MLP and attention layers.
S is the number of tokens we're conditioning on, T is the number of tokens we're generating.
Later, we'll specialize to prefill (T = S) and generation (T = 1).
对于MLP来说,推理时可以通过增加batchsize来提高效率,也就是将多个用户的prompt进行batch,然后同时进行prefill和generation。
For the two stages:
对于attention来说,无法通过增加batchsize来提高效率,因为每个sequence都有自己的kvcache,增加batchisize,相应的kv cache也增加了。
Unlike MLPs, no dependence on B, so batching doesn't help。
Why?
Summary
Tradeoff between latency and throughput:
Easy parallelism: if you launch M copies of the model, latency is the same, throughput increases by M!
Harder parallelism: shard the model and the KV cache [Scaling book chapter on Transformers] kv cache也要进行shard
如何提升推理速度?
1.减少kv cache
推理的主要瓶颈是kv cache,memory limited,所以内存占用越小,速度越快(因为涉及和HBM的传输),速度与内存直接相关。
MQA和GQA,n个头的query对应单个或m(m小于n)个key和value,这样就不用存n个头的key和value了,只存一个头的key和value就行了。
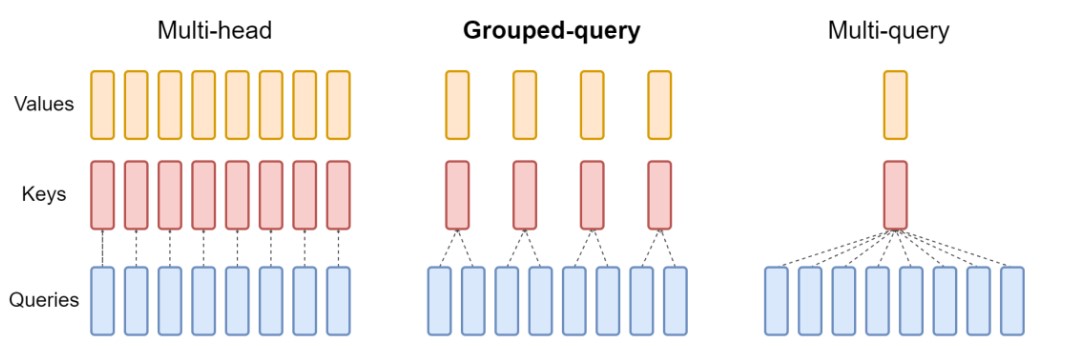
除了速度提升,减少kv-cache的另一个附带好处是,内存占用更小了,同样大小的内存可以装入更大的batchsize,这样进一步提高了throughput。
Deepseek MLA
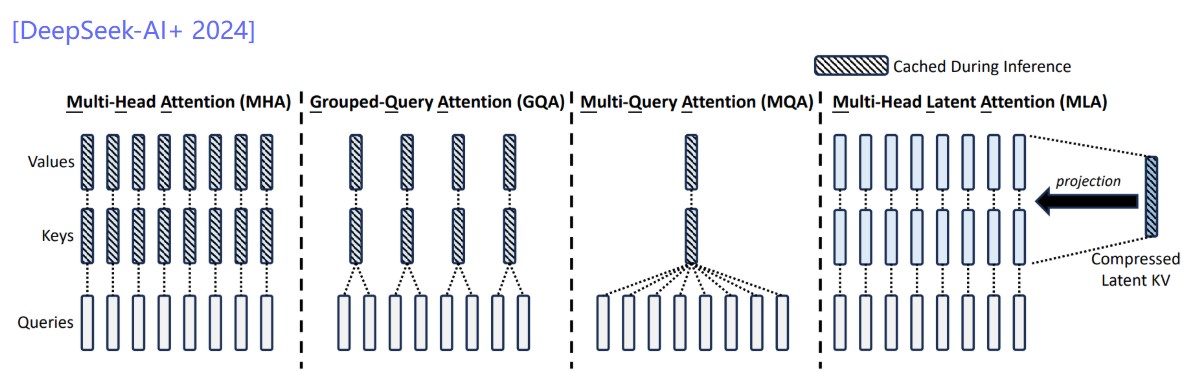
Key idea: project down each key and value vector from N*H dimensions to C dimensions
DeepSeek v2: reduce N*H = 16384 to C = 512
Wrinkle: MLA is not compatible with RoPE, so need to add additional 64 dimensions for RoPE, so 512 + 64 = 576 total dimensions
Latency/throughput improvements follow similarly from the KV cache reduction as argued earlier
Cross-layer attention (CLA)
GQA是在不同的heads之间共享key和value,CLA是在不同的层之间共享key和value
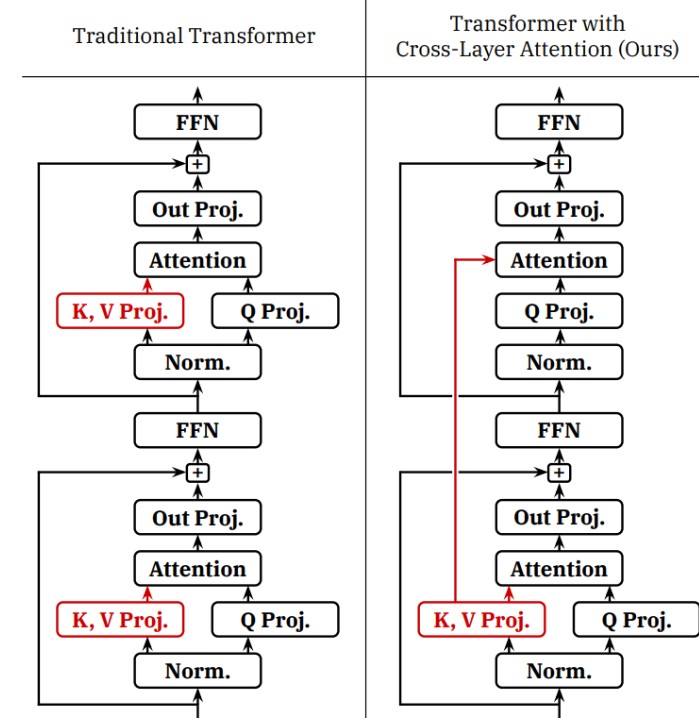
Idea: share KVs across layers (just as GQA shares KVs across heads)
Empirically improves the pareto frontier of accuracy and KV cache size (latency and throughput)
Local attention
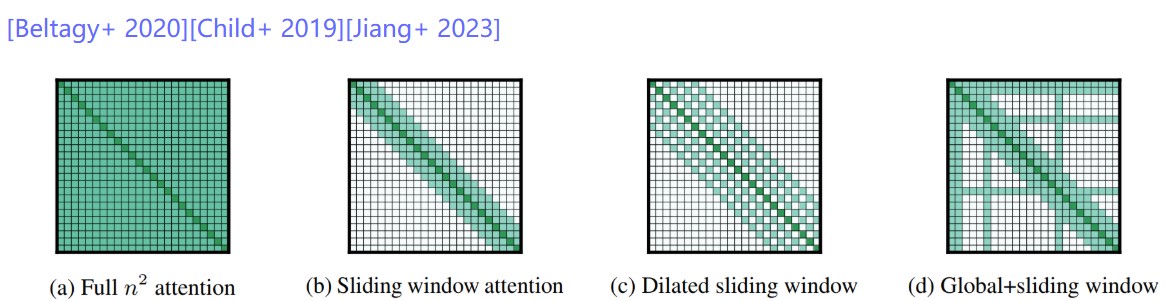
Idea: just look at the local context, which is most relevant for modeling
Effective context scales linearly with the number of layers
KV cache is independent of sequence length!
总结:
Taking shortcuts (lossy)
1.reduce_kv_cache_size()
2.alternatives_to_the_transformer() :State-space models,Diffusion models
3.quantization() : LLM.int8() , Activation-aware quantization
4.model_pruning(): Key idea: just rip out parts of an expensive model to make it cheaper
...and then fix it up.
Use shortcuts but double check (lossless)
speculative_sampling: In other words, checking is faster than generation.
Handling dynamic workloads
Batching over sequences in live traffic is tricky because:
Requests arrive at different times (waiting for batch is bad for early requests)
Sequences have shared prefixes (e.g., system prompts, generating multiple samples
Sequences have different lengths (padding is inefficient)
continuous_batching()
paged_attention(): PageAttention 是一种通过借鉴操作系统分页和内存共享思想,来高效管理LLM推理过程中KV Cache的技术。它是vLLM推理引擎的核心,能极大地提升GPU内存利用率和请求吞吐量。
Other vLLM optimizations: