CS336-2025-lec8
2025年10月24日
10:42
- Collective means that you specify communication pattern across many (e.g., 256) nodes.
- These are classic in the parallel programming literature from the 1980s.
- Better/faster abstraction than managing point-to-point communication yourself.
- World size: number of devices (e.g., 4)
- Rank: a device (e.g., 0, 1, 2, 3)
- Reduce: performs some associative/commutative operation (sum, min, max)
- Broadcast/scatter is inverse of gather
- All: means destination is all devices
- Detects topology of hardware (e.g., number of nodes, switches, NVLink/PCIe)
- Optimizes the path between GPUs
- Launches CUDA kernels to send/receive data
- Provides clean interface for collective operations (e.g., all_gather_into_tensor)
- Supports multiple backends for different hardware: gloo (CPU), nccl (GPU
- Also supports higher-level algorithms (e.g., FSDP, FullyShardedDataParallel) [not used in this course]
并行
def collective_operations():
Collective operations are the conceptual primitives used for distributed programming
Terminology:
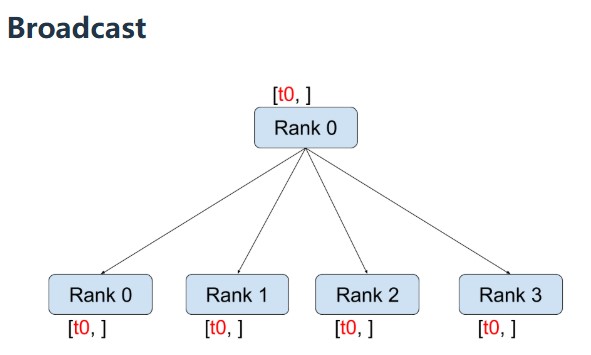
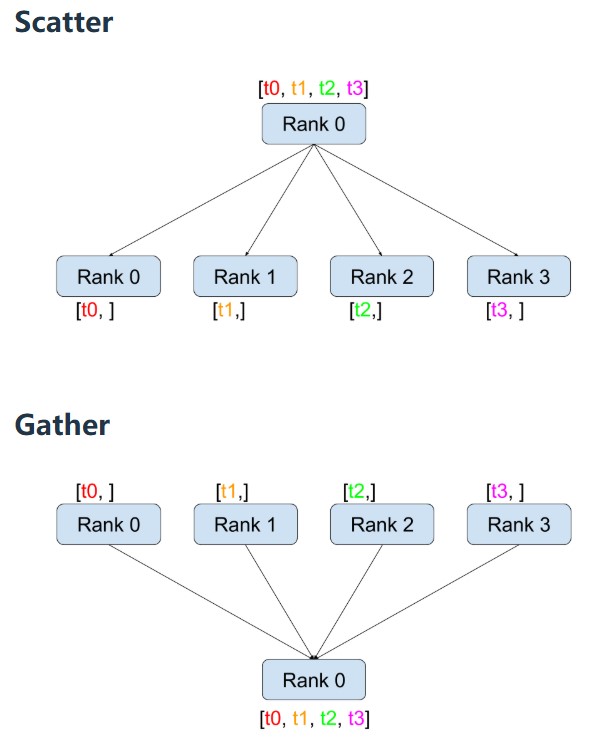
Way to remember the terminology:
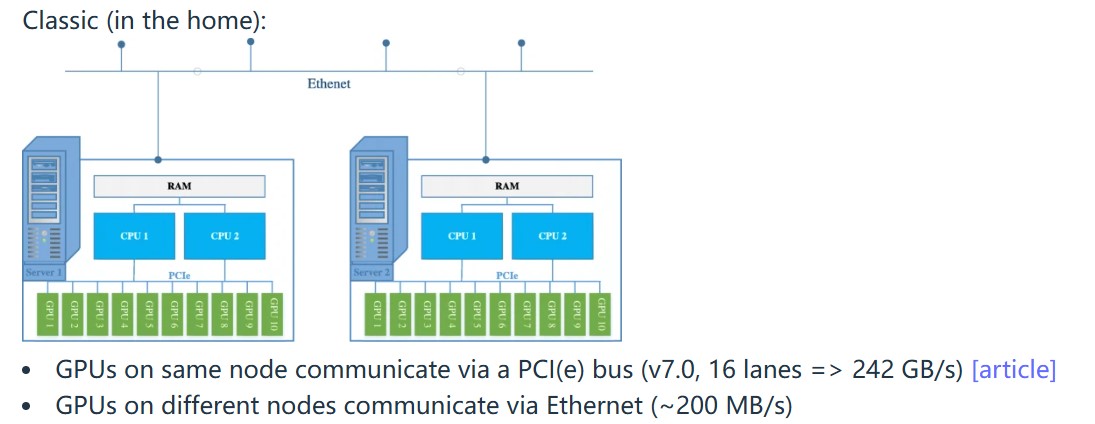
上图是家用的多机模式,同一个node下的GPU通过PCI通信,不同node的GPU通过Ethernet通信。
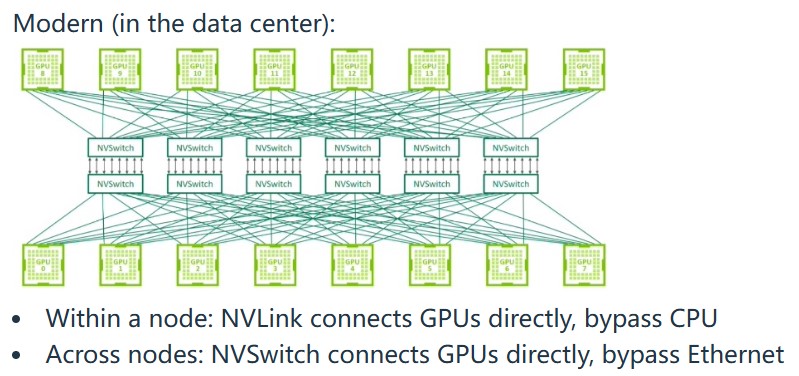
现代数据中心,和家用多机多卡模型不同,通过NVlink和NVSwitch通信,而不是通过CPU和Ethernet通信。
NVIDIA Collective Communication Library (NCCL)
NCCL translates collective operations into low-level packets that are sent between GPUs.
PyTorch distributed library (torch.distributed)更高level来调用nccl,例如直接用dist.all_gather
def collective_operations_main(rank: int, world_size: int):
"""This function is running asynchronously for each process (rank = 0, ..., world_size - 1)."""
setup(rank, world_size)
# All-reduce
dist.barrier() # Waits for all processes to get to this point (in this case, for print statements)
tensor = torch.tensor([0., 1, 2, 3], device=get_device(rank)) + rank # Both input and output
print(f"Rank {rank} [before all-reduce]: {tensor}", flush=True)
dist.all_reduce(tensor=tensor, op=dist.ReduceOp.SUM, async_op=False) # Modifies tensor in place
print(f"Rank {rank} [after all-reduce]: {tensor}", flush=True)
# Reduce-scatter
dist.barrier()
input = torch.arange(world_size, dtype=torch.float32, device=get_device(rank)) + rank # Input
output = torch.empty(1, device=get_device(rank)) # Allocate output
print(f"Rank {rank} [before reduce-scatter]: input = {input}, output = {output}", flush=True)
dist.reduce_scatter_tensor(output=output, input=input, op=dist.ReduceOp.SUM, async_op=False)
print(f"Rank {rank} [after reduce-scatter]: input = {input}, output = {output}", flush=True)
# All-gather
dist.barrier()
input = output # Input is the output of reduce-scatter
output = torch.empty(world_size, device=get_device(rank)) # Allocate output
print(f"Rank {rank} [before all-gather]: input = {input}, output = {output}", flush=True)
dist.all_gather_into_tensor(output_tensor=output, input_tensor=input, async_op=False)
print(f"Rank {rank} [after all-gather]: input = {input}, output = {output}", flush=True)
Indeed, all-reduce = reduce-scatter + all-gather!
cleanup()
def data_parallelism_main(rank: int, world_size: int, data: torch.Tensor, num_layers: int, num_steps: int):
setup(rank, world_size)
# Get the slice of data for this rank (in practice, each rank should load only its own data)
batch_size = data.size(0) # @inspect batch_size
num_dim = data.size(1) # @inspect num_dim
local_batch_size = int_divide(batch_size, world_size) # @inspect local_batch_size
start_index = rank * local_batch_size # @inspect start_index
end_index = start_index + local_batch_size # @inspect end_index
data = data[start_index:end_index].to(get_device(rank)) #每个device根据不同的索引取数据
# Create MLP parameters params[0], ..., params[num_layers - 1] (each rank has all parameters)
params = [get_init_params(num_dim, num_dim, rank) for i in range(num_layers)]
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(params, lr=1e-3) # Each rank has own optimizer state
for step in range(num_steps):
# Forward pass
x = data
for param in params:
x = x @ param
x = F.gelu(x)
loss = x.square().mean() # Loss function is average squared magnitude
# Backward pass
loss.backward()
# Sync gradients across workers (only difference between standard training and DDP)
for param in params:
dist.all_reduce(tensor=param.grad, op=dist.ReduceOp.AVG, async_op=False)#所有参数的梯度进行同步,计算所有device的梯度平均值。
# Update parameters
optimizer.step()
print(f"[data_parallelism] Rank {rank}: step = {step}, loss = {loss.item()}, params = {[summarize_tensor(params[i]) for i in range(num_layers)]}", flush=True)
cleanup()
Tensor parallel
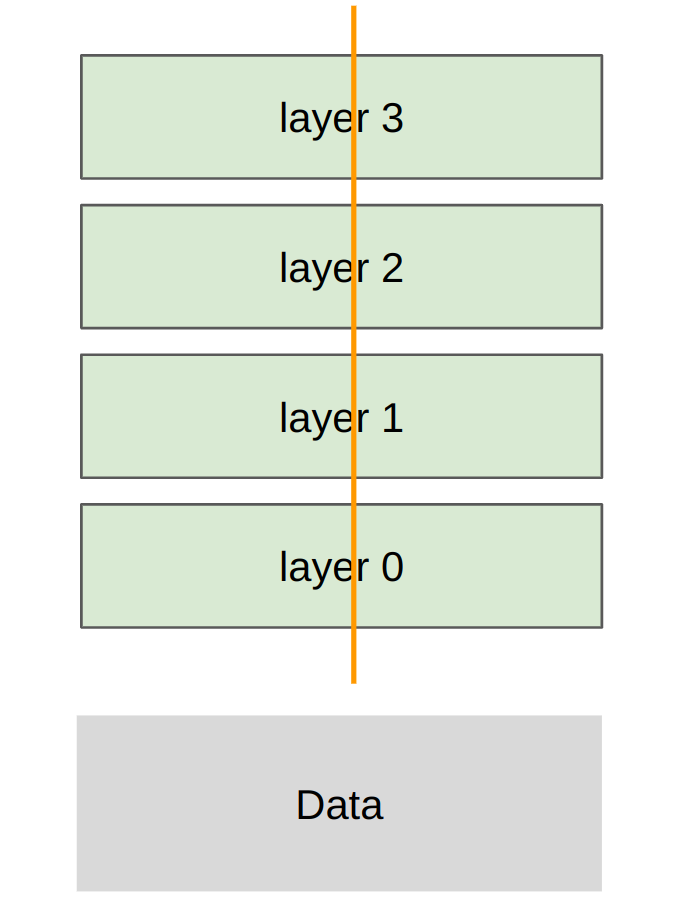
Sharding strategy: each rank gets part of each layer, transfer all data/activations
def tensor_parallelism_main(rank: int, world_size: int, data: torch.Tensor, num_layers: int):
setup(rank, world_size)
data = data.to(get_device(rank))
batch_size = data.size(0) # @inspect batch_size
num_dim = data.size(1) # @inspect num_dim
local_num_dim = int_divide(num_dim, world_size) # Shard `num_dim` @inspect local_num_dim
#对num_dim进行切分 ,每个device有local_num_dim
# Create model (each rank gets 1/world_size of the parameters)
params = [get_init_params(num_dim, local_num_dim, rank) for i in range(num_layers)]
# Forward pass
x = data
for i in range(num_layers):
# Compute activations (batch_size x local_num_dim)
x = x @ params[i] # Note: this is only on a slice of the parameters
x = F.gelu(x)
# Allocate memory for activations (world_size x batch_size x local_num_dim)
activations = [torch.empty(batch_size, local_num_dim, device=get_device(rank)) for _ in range(world_size)]
# Send activations via all gather
dist.all_gather(tensor_list=activations, tensor=x, async_op=False) #模型的每一层都要all_gather所有device的activations
# Concatenate them to get batch_size x num_dim
x = torch.cat(activations, dim=1) #然后进行concat
print(f"[tensor_parallelism] Rank {rank}: forward pass produced activations {summarize_tensor(x)}", flush=True)
# Backward pass: homework exercise
cleanup()
Pipeline parallel
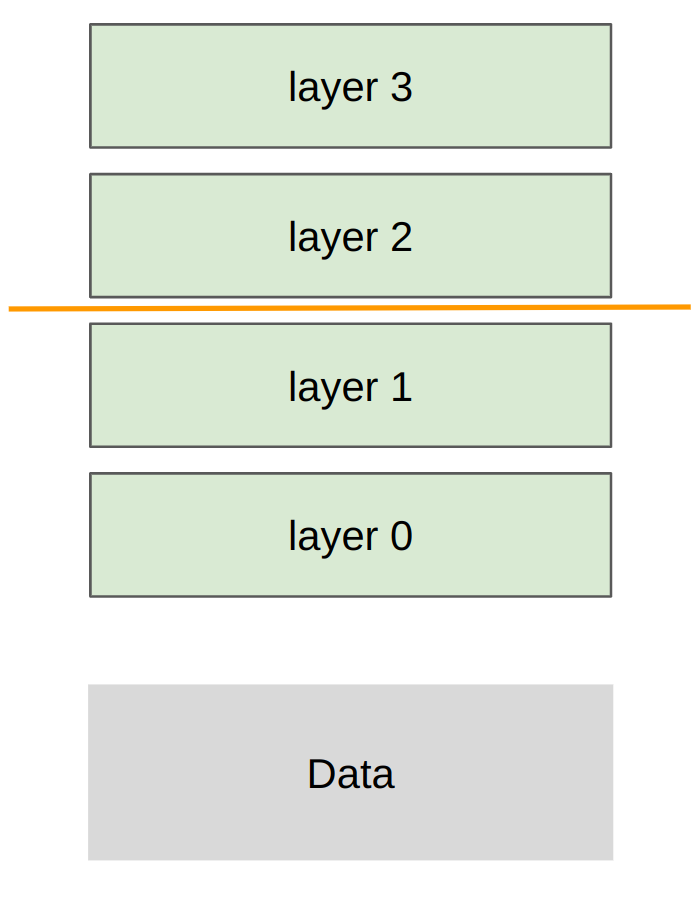
Sharding strategy: each rank gets subset of layers, transfer all data/activations
def pipeline_parallelism_main(rank: int, world_size: int, data: torch.Tensor, num_layers: int, num_micro_batches: int):
setup(rank, world_size)
# Use all the data
data = data.to(get_device(rank))
batch_size = data.size(0) # @inspect batch_size
num_dim = data.size(1) # @inspect num_dim
# Split up layers
local_num_layers = int_divide(num_layers, world_size) # @inspect local_num_layers
#假设整个模型有12层,worldsize=4,那么每个device有3层
# Each rank gets a subset of layers
local_params = [get_init_params(num_dim, num_dim, rank) for i in range(local_num_layers)]
# Forward pass
# Break up into micro batches to minimize the bubble
micro_batch_size = int_divide(batch_size, num_micro_batches) # @inspect micro_batch_size
if rank == 0:
# The data
micro_batches = data.chunk(chunks=num_micro_batches, dim=0)
else:
# Allocate memory for activations
micro_batches = [torch.empty(micro_batch_size, num_dim, device=get_device(rank)) for _ in range(num_micro_batches)]
for x in micro_batches:
# Get activations from previous rank
if rank - 1 >= 0:
dist.recv(tensor=x, src=rank - 1)
# Compute layers assigned to this rank
for param in local_params:
x = x @ param
x = F.gelu(x)
# Send to the next rank
if rank + 1 < world_size:
print(f"[pipeline_parallelism] Rank {rank}: sending {summarize_tensor(x)} to rank {rank + 1}", flush=True)
dist.send(tensor=x, dst=rank + 1)
Not handled: overlapping communication/computation to eliminate pipeline bubbles
# Backward pass: homework exercise
cleanup()